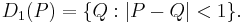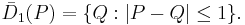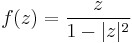Unit disk
In mathematics, the open unit disk (or disc) around P (where P is a given point in the plane), is the set of points whose distance from P is less than 1:
The closed unit disk around P is the set of points whose distance from P is less than or equal to one:
Unit disks are special cases of disks and unit balls.
Without further specifications, the term unit disk is used for the open unit disk about the origin, 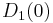 , with respect to the standard Euclidean metric. It is the interior of a circle of radius 1, centered at the origin. This set can be identified with the set of all complex numbers of absolute value less than one. When viewed as a subset of the complex plane (C), the unit disk is often denoted
, with respect to the standard Euclidean metric. It is the interior of a circle of radius 1, centered at the origin. This set can be identified with the set of all complex numbers of absolute value less than one. When viewed as a subset of the complex plane (C), the unit disk is often denoted 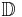 .
.
Contents |
The open unit disk, the plane, and the upper half-plane
The function
is an example of a real analytic and bijective function from the open unit disk to the plane; its inverse function is also analytic. Considered as a real 2-dimensional analytic manifold, the open unit disk is therefore isomorphic to the whole plane. In particular, the open unit disk is homeomorphic to the whole plane.
There is however no conformal bijective map between the open unit disk and the plane. Considered as a Riemann surface, the open unit disk is therefore different from the complex plane.
There are conformal bijective maps between the open unit disk and the open upper half-plane. So considered as a Riemann surface, the open unit disk is isomorphic ("biholomorphic", or "conformally equivalent") to the upper half-plane, and the two are often used interchangeably.
Much more generally, the Riemann mapping theorem states that every simply connected open subset of the complex plane that is different from the complex plane itself admits a conformal and bijective map to the open unit disk.
One bijective conformal map from the open unit disk to the open upper half-plane is the Möbius transformation
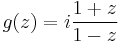 which is the inverse of the Cayley transform.
which is the inverse of the Cayley transform.
Geometrically, one can imagine the real axis being bent and shrunk so that the upper half-plane becomes the disk's interior and the real axis forms the disk's circumference, save for one point at the top, the "point at infinity". A bijective conformal map from the open unit disk to the open upper half-plane can also be constructed as the composition of two stereographic projections: first the unit disk is stereographically projected upward onto the unit upper half-sphere, taking the "south-pole" of the unit sphere as the projection center, and then this half-sphere is projected sideways onto a vertical half-plane touching the sphere, taking the point on the half-sphere opposite to the touching point as projection center.
The unit disk and the upper half-plane are not interchangeable as domains for Hardy spaces. Contributing to this difference is the fact that the unit circle has finite (one-dimensional) Lebesgue measure while the real line does not.
Hyperbolic space
The open unit disk is commonly used as a model for the hyperbolic plane, by introducing a new metric on it, the Poincaré metric. Using the above mentioned conformal map between the open unit disk and the upper half-plane, this model can be turned into the Poincaré half-plane model of the hyperbolic plane. Both the Poincaré disk and the Poincaré half-plane are conformal models of hyperbolic space, i.e. angles measured in the model coincide with angles in hyperbolic space, and consequently the shapes (but not the sizes) of small figures are preserved.
Another model of hyperbolic space is also built on the open unit disk: the Klein model. It is not conformal, but has the property that straight lines in the model correspond to straight lines in hyperbolic space.
Unit disks with respect to other metrics
One also considers unit disks with respect to other metrics. For instance, with the taxicab metric and the Chebyshev metric disks look like squares (even though the underlying topologies are the same as the Euclidean one).
The area of the Euclidean unit disk is π and its perimeter is 2π. In contrast, the perimeter (relative to the taxicab metric) of the unit disk in the taxicab geometry is 8. In 1932, Stanisław Gołąb proved that in metrics arising from a norm, the perimeter of the unit disk can take any value in between 6 and 8, and that these extremal values are obtained if and only if the unit disk is a regular hexagon or a parallelogram, respectively.
See also
References
- S. Golab, "Quelques problèmes métriques de la géometrie de Minkowski", Trav. de l'Acad. Mines Cracovie 6 (1932), 179.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Unit disk" from MathWorld.
- On the Perimeter and Area of the Unit Disc, by J.C. Álvarez Pavia and A.C. Thompson